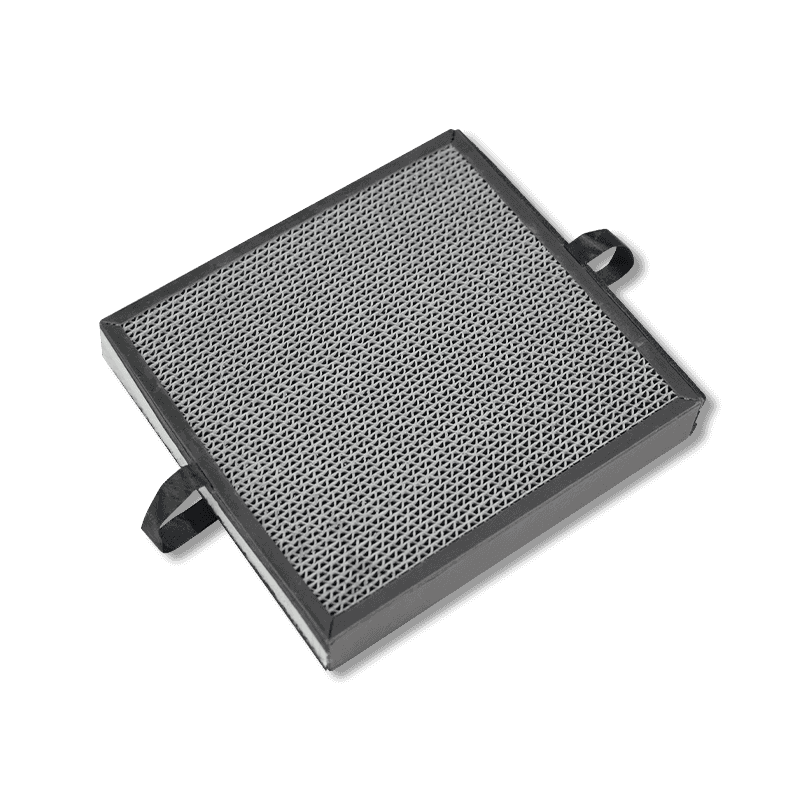
1. How Activated Carbon Filters Work
Activated carbon is a porous material, typically made from carbonized organic matter (such as wood, coconut shells, or coal), possessing an extremely high specific surface area (hundreds of square meters per gram of activated carbon). Its main working principle is to remove airborne pollutants through adsorption. Specifically, activated carbon filters remove pollutants in the following ways:
Gas Adsorption: The micropores on the surface of activated carbon can adsorb and capture gas molecules, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon dioxide. Some harmful gases from vehicle emissions (such as benzene, formaldehyde, and hydrogen sulfide) can be removed in this way.
Particulate Adsorption: The surface structure of activated carbon can also adsorb some tiny particles in the air, but this is mainly effective for extremely fine particles (such as dust or pollutants in the air) and is not effective at removing larger or heavier particles (such as black smoke particles from diesel engines).
The main advantage of activated carbon filters is the removal of gaseous pollutants, but it cannot completely replace other types of filtration technologies, especially when dealing with larger particles or high concentrations of pollutants.

2. Effectiveness of Activated Carbon Filters in Vehicle Emissions
Removal of Gaseous Pollutants:
Activated carbon filters perform well in removing some harmful gases, especially gaseous pollutants related to vehicle emissions. Specifically:
Carbon Monoxide (CO):Carbon monoxide is a common gas in vehicle emissions. It is colorless and odorless, but toxic to humans. Activated carbon effectively adsorbs carbon monoxide, reducing its concentration in the air.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx):Activated carbon has some adsorption capacity for some nitrogen oxides (NOx), especially those produced in vehicle exhaust. Although its efficiency is not as high as dedicated catalytic reduction equipment, it can still play a role in reducing NOx levels.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):Many volatile organic compounds are harmful components in vehicle exhaust, such as benzene, toluene, and ethylbenzene. These gases can be removed through the adsorption of activated carbon, thereby improving air quality.
Particulate Matter Removal:
However, activated carbon is less effective at removing **particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10)** from emissions. Particulate matter emitted by vehicles is typically controlled and reduced through mechanical devices (such as diesel particulate filters), not activated carbon filters.
Particulate matter, especially fine PM2.5 and PM10, is harmful to human health, and long-term exposure can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. While activated carbon can be effective against some larger particles, its filtration efficiency is generally insufficient for high-level applications.
3. Applications in Vehicles
Activated carbon filters are primarily used for purifying in-vehicle air and reducing the entry of external pollutants into the vehicle, but they are not a core technology for emissions pollution control. Specific applications include: In-vehicle air filters: Many modern cars are equipped with activated carbon in-vehicle air filters, which effectively reduce the entry of harmful gases from the outside air (such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide) into the vehicle. Drivers can improve the air quality inside the car using this filter, especially on heavily polluted urban roads. It also removes odors, smoke, dust, etc. from outside the vehicle.
Filtration of external pollution: Since external pollution sources (such as exhaust emissions) are usually difficult to completely remove directly by filters, activated carbon filters are limited to filtering out harmful gases and are insufficient to fundamentally control external air pollution.
4. Potential Applications and Prospects of Activated Carbon in Vehicle Emission Control
While activated carbon is not the only solution for vehicle emission control, it does hold potential in certain areas, particularly in improving air quality and reducing harmful gas emissions. With increasing environmental demands, activated carbon technology may be combined with other emission control technologies to play a greater role.
Potential in In-Vehicle Air Purification
Activated carbon filters are already widely used in in-vehicle air purification, and their application is expected to expand further as in-vehicle air quality requirements continue to rise. Vehicle air purification is not just about removing odors and dust; more and more automakers are focusing on filtering harmful gases (such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds) from the vehicle interior.
Enhancing In-Vehicle Air Quality: By combining high-efficiency activated carbon with HEPA filtration technology, activated carbon can effectively remove harmful gases from outside the vehicle, especially in heavily polluted urban environments. Activated carbon filters can reduce the concentration of toxic gases in the in-vehicle air, improving the driving experience and health protection for drivers.
Intelligentization and Multifunctionality: In the future, activated carbon filtration technology may be combined with in-vehicle air quality monitoring systems to intelligently regulate in-vehicle air quality. For example, when outside air pollution worsens, the vehicle's air filtration system can automatically activate a more efficient activated carbon filtration mode to provide better air purification.
Potential Role in Emission Systems
Although activated carbon is not currently a primary vehicle emission control technology, its role in emission systems may expand with technological advancements. Especially in reducing the emission of certain pollutants (such as harmful gases), activated carbon could serve as an auxiliary means, working in conjunction with other advanced emission treatment technologies to further reduce harmful components in vehicle exhaust.
Assisting Catalytic Converters: During the operation of catalytic converters, activated carbon may serve as an auxiliary material to capture some incompletely converted harmful gases in vehicle emissions. For example, it can adsorb organic gases that are difficult for catalysts to handle, further improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle emission system.
Adsorbing Harmful Gases: For certain gases in vehicle exhaust (such as hydrogen sulfide and benzene), activated carbon may be able to directly pre-treat them through adsorption, reducing the concentration of these harmful substances in vehicle emissions, thereby reducing the pollution load of exhaust gases.
Enhancing Emission Control for Environmentally Friendly Vehicles
With increasingly stringent global environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and North America, vehicle emission requirements are becoming more stringent. Activated carbon is likely to become a crucial component of emission control systems in future environmentally friendly vehicles, especially in certain emerging green technologies, where it can provide additional environmental advantages.
Combined Applications in Electric Vehicles and Hybrid Vehicles: In the development of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), activated carbon filtration technology may be combined with battery technology and other environmentally friendly technologies to provide a more comprehensive pollution control solution. For example, activated carbon can be used to adsorb organic solvents or gases that may be released during the use of electric vehicles, helping to improve in-vehicle air quality.
Applications in Renewable Energy Vehicles: For vehicles using natural gas or biofuels (such as biodiesel, biogas, etc.), activated carbon filters may help remove harmful gases produced during fuel combustion, further optimizing the emission performance of these environmentally friendly fuels.
Future Outlook: Combining Activated Carbon with Other Green Technologies
With continuous technological advancements, the possibility of combining activated carbon technology with other green technologies (such as photocatalysis, nanomaterials, advanced materials, etc.) is increasing. Combining the advantages of different technologies may lead to more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicle emission control solutions in the future. Combining Nanomaterials with Activated Carbon: Nanotechnology has made some progress in its application to filter materials. Combining activated carbon with nanomaterials can enhance its adsorption capacity and improve its ability to treat specific pollutants (such as nitrogen oxides and ozone). In this way, the emission control efficiency of activated carbon is expected to be further improved.
Combining Photocatalysis with Activated Carbon: Photocatalysis can activate catalysts to decompose harmful gases in the air using ultraviolet light. When activated carbon is combined with photocatalytic materials, its ability to remove harmful gases under sunlight is enhanced, making it particularly suitable for use in environments requiring continuous air purification.

 English
English Español
Español 日本語
日本語