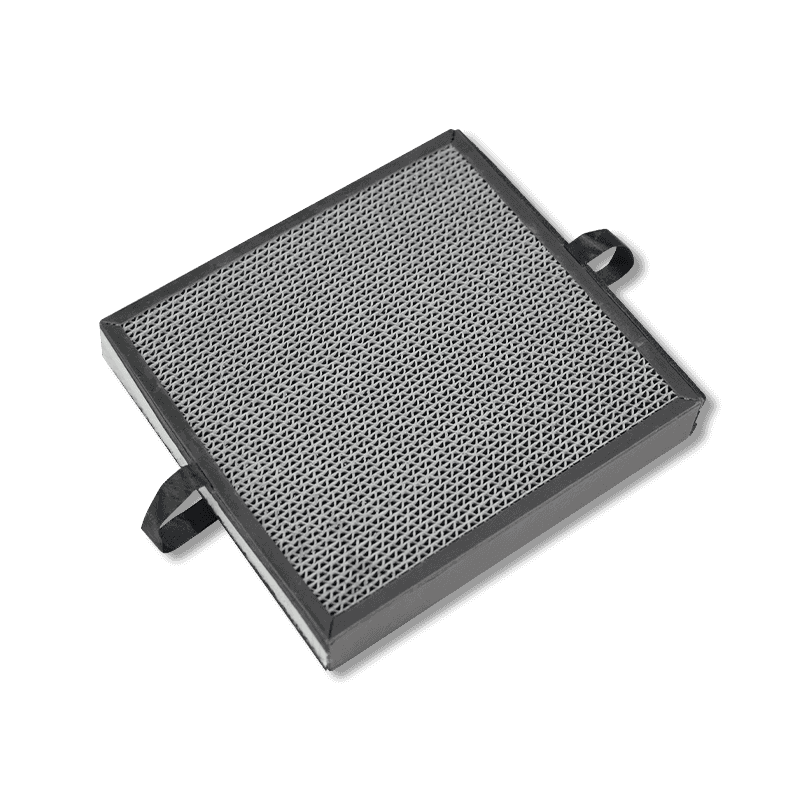
1. The Core Role of Air Filters in Air Purifiers
The working principle of an air purifier is to filter various pollutants from the air to improve indoor air quality and ensure people breathe fresh, healthy air. As the core consumable of the air purifier, the role of air filters cannot be underestimated. Different types of air filters can filter various pollutants in the air, such as dust, pollen, smoke, pet hair, bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances. The effectiveness of an air purifier is directly related to the design and performance of the filters, so choosing the right filter is crucial.
Working Principle of Air Purifiers
The typical workflow of an air purifier involves a fan drawing indoor air into the machine, which then passes through multiple layers of filters before being expelled as purified air. The air filter plays a critical role in this process. It effectively prevents pollutants in the air from re-entering the indoor environment. Depending on the usage environment, air purifiers may use different combinations of filters. The most common types are HEPA filters, activated carbon filters.
HEPA filters primarily filter out fine particulate matter, such as dust mites, pollen, and bacteria, while activated carbon filters focus on removing harmful gases, such as kitchen smoke, formaldehyde, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). on the other hand, kill bacteria and viruses in the air to enhance the purifying effect.
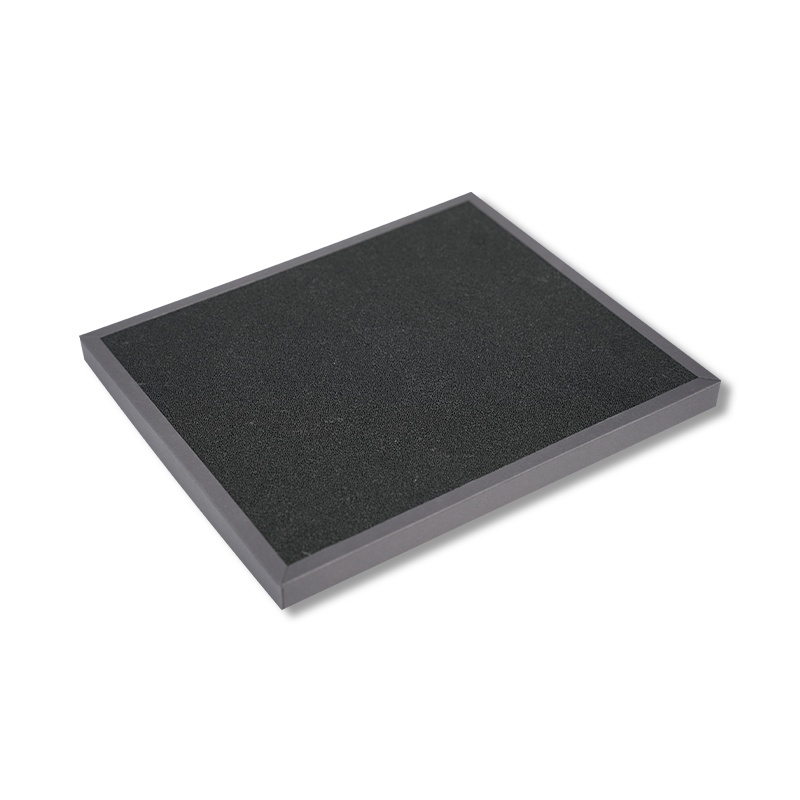
The Role and Importance of Air Filters
Air filters do more than just remove particulate matter from the air; they also eliminate harmful gases, odors, and microorganisms. If air filters are not replaced or maintained in time, they will not function effectively, causing the air purifier to lose its intended effect. Over time, filters become saturated with pollutants, causing them to lose their efficacy. Therefore, understanding the filter’s lifespan, working principle, and maintenance methods is crucial to maintaining the air purifier’s performance.
2. Types of Air Filters and Their Working Principles
There are numerous types of air filters available on the market, each designed to address specific air pollution issues. Understanding the working principles and characteristics of these filters helps consumers make informed decisions when purchasing air purifiers.
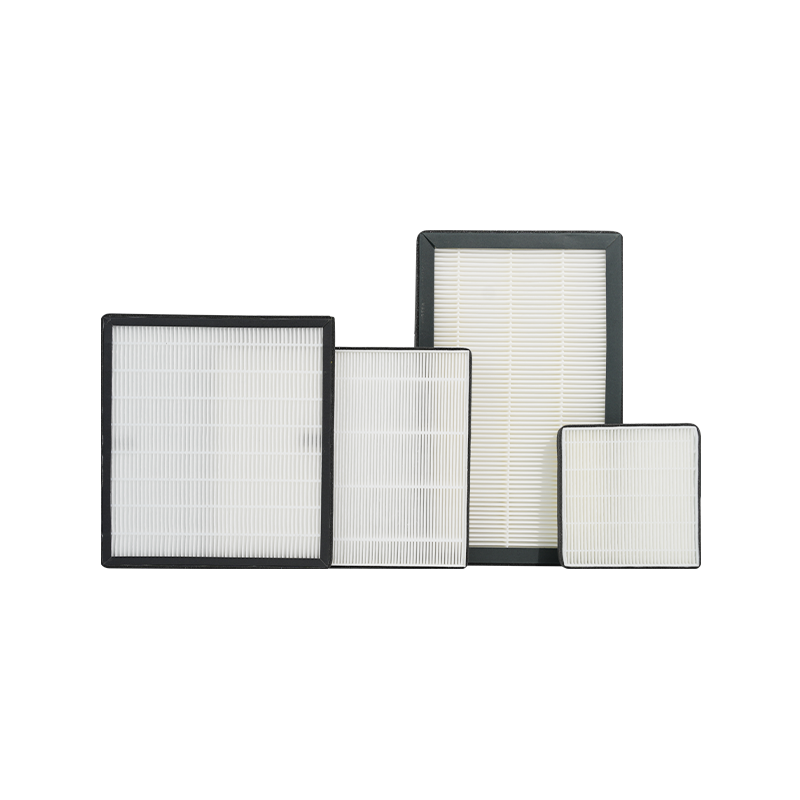
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters
HEPA filters are one of the most common and effective types of particulate filters used in air purifiers. The primary advantage of HEPA filters is their ability to filter particles as small as 0.3 microns with a filtration efficiency of 99.97%. These filters can capture fine particles in the air, such as dust, pollen, pet dander, and mold spores, making them ideal for people with allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions.
The working principle of HEPA filters is based on a series of interwoven fibers that form a dense filter network. When air flows through the filter, tiny particles are trapped on the fiber surface and cannot pass through. HEPA filters provide stable and effective filtration but gradually become clogged with use, which reduces airflow. Therefore, they need to be replaced periodically.
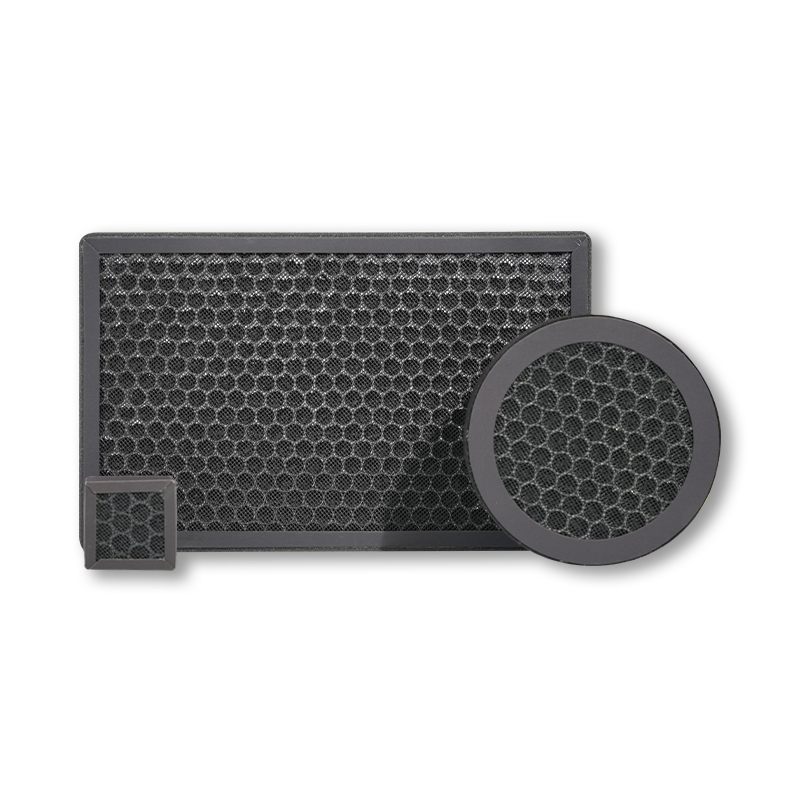
Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon filters are primarily used to adsorb harmful gases, odors, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the air, such as formaldehyde, second-hand smoke, and kitchen fumes. The working principle of activated carbon filters is based on adsorption. Activated carbon has a vast surface area and a porous structure that allows it to effectively trap harmful gases in the air. Unlike HEPA filters, which primarily target particulate matter, activated carbon filters focus on removing gases and odors. Activated carbon filters are often used in conjunction with HEPA filters to create a comprehensive air purification system that removes both particulate matter and harmful gases.
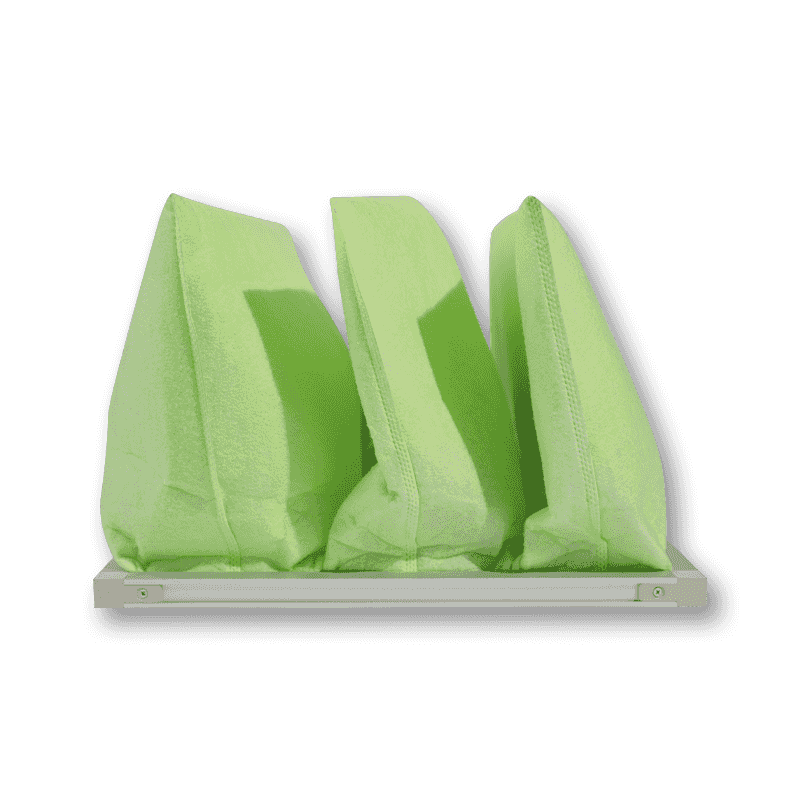
Pre-filters
Pre-filters are used in air purifiers to capture larger particles such as hair, dust, and pet fur. The role of the pre-filter is to reduce the burden on the main filter, thus extending the lifespan of HEPA or activated carbon filters. Pre-filters typically use mesh or sponge materials to capture larger particles. They not only help improve the efficiency of the air purifier but also reduce the frequency of replacing the main filters.
3. The Working Principles of Air Filters and Their Impact on Air Quality
The working principles of air filters rely on a variety of physical and chemical mechanisms that work together to ensure the air purifier can efficiently remove pollutants from the air. Different filters are designed to target different pollutants, which directly affects the performance of the air purifier. The effectiveness of the filter directly determines whether the air purifier will achieve the desired air quality improvement.
Physical Filtration
Physical filtration is the most common filtering method in air purifiers, primarily relying on mesh or filter materials in the filter to physically block particulate matter from the air. HEPA filters are a typical example of physical filtration. They consist of dense fibers that trap small particles in the air as it passes through. This method is especially effective at removing dust, pollen, bacteria, mold spores, and other particulate matter. The advantage of physical filtration is its stability and effectiveness, but over time, filters become clogged with pollutants, which reduces their filtration efficiency.
Adsorption
The working principle of activated carbon filters is based on adsorption, which removes gaseous pollutants from the air. The porous structure of activated carbon provides a vast surface area for adsorbing harmful gases and chemicals. Unlike physical filtration, adsorption targets gaseous pollutants, such as formaldehyde, second-hand smoke, and VOCs. This method is highly effective for odor removal and harmful gas filtration. The downside is that activated carbon has a limited adsorption capacity, and once its surface area becomes saturated with pollutants, its effectiveness decreases, requiring replacement.
Electrostatic Attraction
Electrostatic attraction is a method used by electrostatic or ionizing filters to attract charged particles in the air. These filters use an electric charge to attract airborne particles such as smoke and dust. The advantage of electrostatic attraction is that it can filter out very fine particles without significantly affecting the airflow. However, this method is less effective at removing harmful gases, so it is often used in combination with other filter types to provide comprehensive air purification.
4. The Lifespan and Maintenance of Air Filters
The lifespan of air filters varies depending on the type, usage frequency, and air quality. Regular inspection and replacement of filters are essential for maintaining the air purifier’s efficiency.
Filter Lifespan
HEPA and activated carbon filters typically last 6 months to 1 year. Activated carbon filters may need to be replaced sooner if they are exposed to high levels of pollutants. Pre-filters can usually be cleaned multiple times and reused, but they should still be checked regularly for cleanliness. UV-C filters have a lifespan depending on the UV light bulbs, typically lasting 1 to 2 years.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular cleaning is necessary to ensure optimal performance of the air purifier. Pre-filters should be cleaned monthly to remove large particles. HEPA and activated carbon filters generally cannot be cleaned, but they should be checked periodically to see if they need replacement. The air purifier’s intake and fan should be kept clean to prevent dust buildup that could affect airflow.

 English
English Español
Español 日本語
日本語