As air quality has received more and more attention, air filter materials have become an indispensable part of people's daily life and industrial production. From home air purifiers to cold storage, fresh air systems, hospitals, food processing workshops and other places with strict requirements for clean air, the stability of air filter materials is directly related to the reliability of air purification effects. The performance stability of filter materials under extreme climatic conditions has gradually become an important consideration in procurement and project implementation.
Many B-end customers worry: Will the air filter "fail" at low temperatures? Will the filtration efficiency decrease? Will the material become brittle, deformed, or will the wind resistance increase sharply? This article will combine Lyusen Environmental Protection's multiple filtration products to systematically analyze the performance and selection recommendations of different air filter materials in low temperature environments, helping you to deploy air purification solutions for cold regions with more peace of mind.
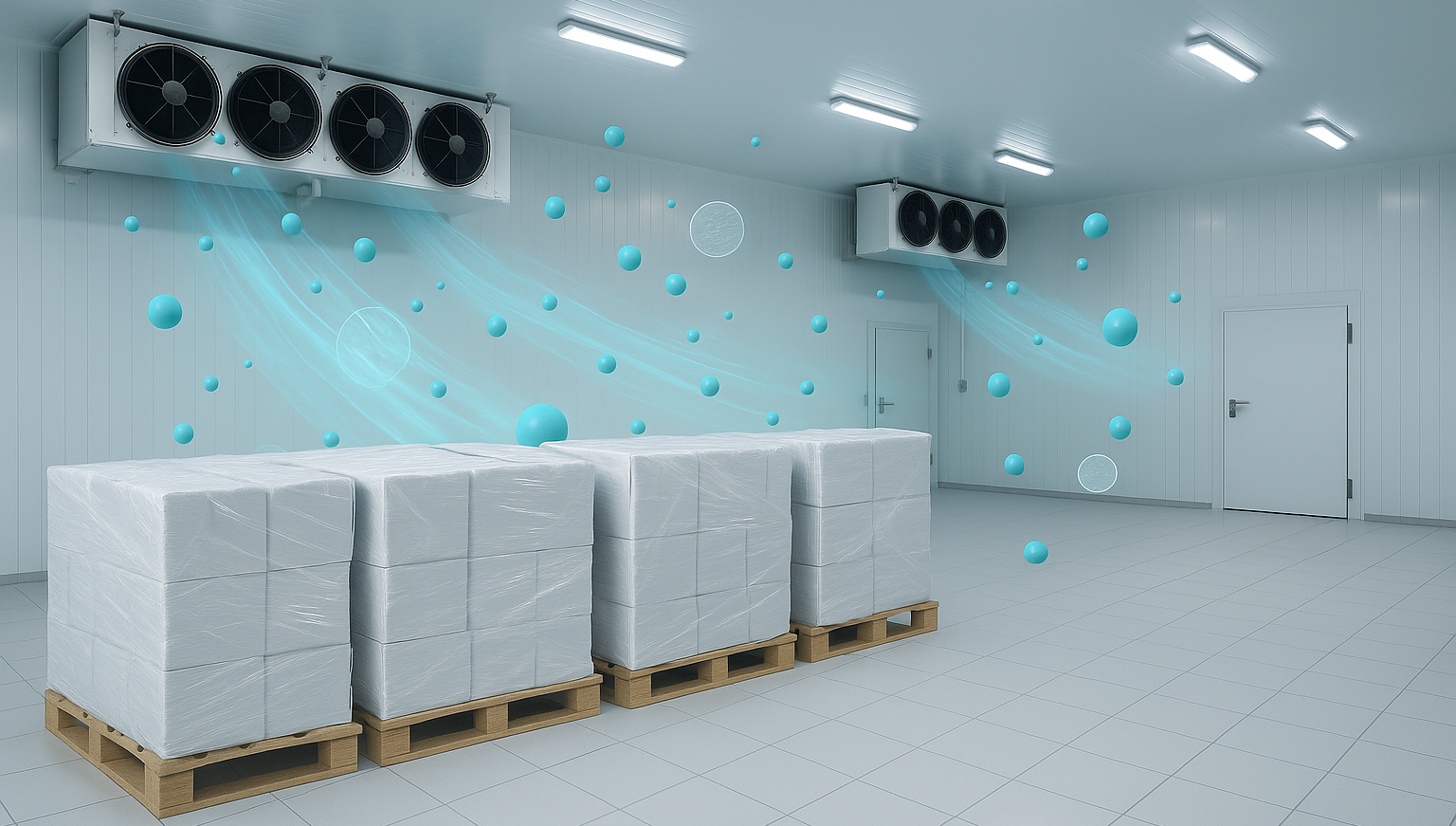

Typical effects of low temperature environment on air filter materials
Low temperature itself will not directly cause the filter material to "fail", but it may indeed affect its performance in the following aspects:
Material embrittlement: Some plastic frames or foam substrates may harden and crack at low temperatures, affecting structural integrity.
Increased wind resistance: The decrease in temperature causes changes in air density, which, combined with moisture condensation, may cause a slight increase in the wind resistance of the filter, thereby affecting the ventilation efficiency of the system.
Changes in adsorption capacity: The adsorption efficiency of some activated carbon materials decreases slowly at low temperatures, especially in environments with high relative humidity.
Fiber structure stability: For filter paper materials such as meltblown and glass fiber, low temperatures usually do not significantly affect their filtration efficiency, but if they coexist with high humidity, the risk of icing or clogging must be prevented.
This "failure" is not a universal phenomenon, and different types of filter materials have different adaptability to low temperatures.
How do different types of filter materials perform at low temperatures?
Fiber filter materials (primary, medium, and high efficiency) - stable structure and reliable performance
This type of filter material is widely used in industrial and civil filtration systems, mainly capturing particulate matter in the air (such as PM2.5, dust, pollen, bacteria, etc.) through electrostatic charging, mechanical interception, and inertial collision.
Common ingredients of materials:
Synthetic polyester fiber (PET/PP)
Glass fiber (commonly used in industrial environments)
Performance at low temperatures:
Most fiber materials still maintain good mechanical strength and shape stability at -20°C or even lower;
The charging performance of electrostatic charging materials is almost unaffected at low temperatures;
The filtration efficiency will not decrease significantly, but the airflow resistance may increase slightly due to the increase in air density.
In low-temperature environments such as cold storage and fresh air systems, fiber filters with reasonable thickness and wind resistance design can still operate stably.
Activated carbon filter material - the adsorption speed slows down, but the effect is not lost
Among many air purification materials, activated carbon filter material is widely used due to its excellent adsorption performance. It is suitable for removing harmful gases such as formaldehyde, benzene, ammonia, TVOC and various odors in the air. It is commonly found in purification equipment in newly renovated environments, odor control inside refrigeration equipment, automobile air conditioning systems, and industrial sites with high requirements for gas cleanliness.
The reason why activated carbon can purify the air efficiently is mainly due to its unique microporous structure. Each gram of activated carbon has a specific surface area of up to thousands of square meters, which can adsorb a large number of gas molecules like a sponge. This physical adsorption mechanism does not rely on chemical reactions, so it can maintain good stability under various temperature and humidity conditions.
However, in low temperature environments, the movement speed of molecules in the air will slow down, resulting in a lower frequency of contact with the pores on the surface of activated carbon. This means that the rate of adsorption reaction will decrease, especially in environments below -20°C, where the activity of gas molecules is insufficient, and it may take longer to complete the same amount of purification process. This change does not affect the total adsorption capacity of activated carbon, that is, it can still "hold" the same amount of harmful gases, but the speed of "filling" will be slower.
In extremely low temperature environments (such as -30°C or lower), in order to ensure continuous purification effects, it is recommended to appropriately extend the use cycle of the filter material, or increase the amount of filter material to improve the overall purification efficiency. If combined with reasonable wind speed and ventilation design, it can also give full play to its effectiveness in low temperature environments.

Catalyst filter materials (catalysts) - some catalysts are more sensitive to low temperatures
Catalyst filter materials, such as cold catalysts and photocatalysts, are mainly used to decompose formaldehyde, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide and other gaseous pollutants in the air. They usually do not rely on adsorption, but decompose harmful substances into harmless small molecules (water and carbon dioxide) through chemical reactions.
Common catalyst materials:
Cold catalysts (not dependent on light, can catalyze reactions at room temperature)
Photocatalysts (such as titanium dioxide TiO₂, which require ultraviolet light excitation)
Factors affecting low temperature:
The activity of some catalysts is positively correlated with temperature, and low temperature will reduce their reaction rate;
However, modern cold catalyst technology can stabilize the catalytic reaction even at 5°C or even 0°C by compounding a variety of rare earth or metal oxides;
Because photocatalysts rely on ultraviolet excitation, they are suitable for use in sunny areas and have limited application in cold storage.

Antibacterial filter materials - slow down sterilization but still have antibacterial effects
Antibacterial filter materials are widely used in hospitals, food cold chains, pharmaceutical warehouses and other places, and have the effect of inhibiting the growth of bacteria and mold.
Common antibacterial agents:
Silver ions, copper ions
Nano zinc oxide, copper oxide
Photocatalytic antibacterial agents (such as TiO₂)
Performance at low temperatures:
Antibacterial mechanisms such as silver ions rely on the principle of sustained release, that is, slowly releasing metal ions to destroy the cell structure of microorganisms;
At low temperatures, the release rate slows down, but does not stop, especially in a refrigerated environment with high humidity, it can still play a good antibacterial effect;
Structural antibacterial coatings (such as coating nano zinc oxide) have physical sterilization and biofilm blocking functions even in extremely cold environments.
Recommendations for selecting low-temperature filters
For customers with projects in cold climates or special low-temperature environments, we recommend that you focus on the following aspects during the selection and design of air filtration products:
Clearly define the temperature range of the use scenario: In cold chain, outdoor fresh air or in extremely cold areas, the temperature requirements should be clearly defined before ordering, and products within the corresponding working temperature range should be selected.
Pay attention to structural materials and edge sealing methods: metal frames, glass fiber materials, cold-resistant non-woven fabrics and other materials have better stability in low-temperature environments.
Consider combined filtration solutions: If you need to control particulate matter and odor, it is recommended to use a GAC+HEPA composite filter, combined with a front dehumidification and rear electric heating module to improve the overall system reliability.
Keep ventilation and dryness: Low temperature does not mean dryness. Moisture condensation and freezing may block the filter material, especially in cold storage applications with frequent switching on and off or frequent frost at night.
Low temperature is not a problem, choosing the right filter material is the key
Different types of air filter materials have certain differences in physical and functional performance in low temperature environments, but "low temperature failure" is not an inevitable result. On the contrary, as long as environmental factors are fully considered in the product design stage, through scientific material selection, structural optimization and technical matching, air filter materials can still achieve stable, continuous and efficient air purification effects at temperatures of -20°C or even lower.
In low-temperature application scenarios such as cold chain transportation, food cold storage, pharmaceutical warehousing, and building ventilation systems in ice and snow areas, air quality assurance is equally important. This is not only related to environmental hygiene and the quality of goods, but also directly affects the respiratory health of operators and the operating efficiency of equipment.
Therefore, in the face of low-temperature environments, we should pay more attention to the following points:
The low-temperature structural stability of the filter material, whether it is easy to crack and deform;
The ability of functional filter materials to maintain activity at low temperatures;
Whether the overall filtration efficiency still meets the design standards at low temperatures;
Whether there is material testing verification and practical application experience suitable for low-temperature scenarios.
As a professional manufacturer of air filter materials, Lyusen Environmental Protection is committed to providing stable and reliable product solutions for customers under different climatic conditions. We have currently supported multiple export projects in special scenarios such as Northern Europe, Central Asia, plateaus, and cold storage. Our product system covers primary, medium, and high-efficiency filter materials and structured filters. Customers are welcome to customize their selections based on project requirements.

 English
English Español
Español 日本語
日本語