1. What is Activated Carbon?
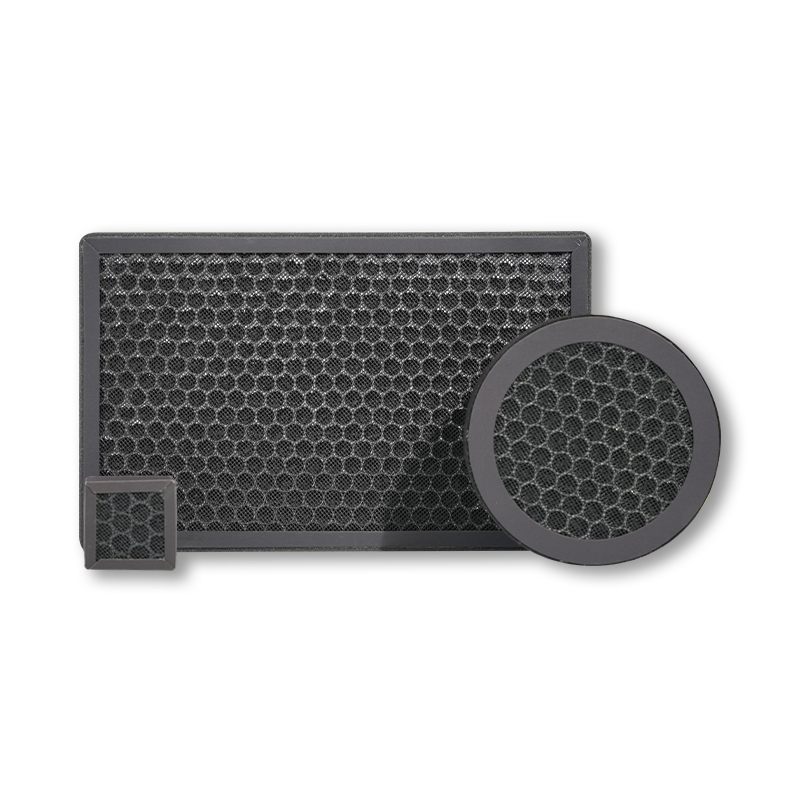
Activated carbon (also known as activated charcoal) is a highly porous material usually derived from organic materials such as wood, coconut shells, or coal through a special process involving heating and treatment with gases. The core feature of activated carbon is its surface, which is filled with millions of tiny pores, making it an excellent material for adsorbing (not absorbing) gases, pollutants, and particulate matter.
In the process of making activated carbon, the raw material is subjected to heat or chemical treatment, which creates a large number of microscopic pores. This treatment significantly increases the surface area of the material, allowing it to trap more molecules or particles in a relatively small volume. Typically, activated carbon has a surface area of hundreds to thousands of square meters per gram. It is these tiny pores and the vast surface area that make activated carbon such an effective adsorbent.
Activated carbon works through two types of adsorption: physical adsorption and chemical adsorption. Physical adsorption involves gas molecules sticking to the surface of the carbon through Van der Waals forces (weak molecular attraction), while chemical adsorption occurs when gas molecules chemically bond with the surface of the carbon. In air purifiers, activated carbon filters mainly rely on physical adsorption to remove odors, gases, and harmful substances from the air.
Activated carbon filters are a critical component in air purifiers. Their adsorption ability allows them to remove not only odors but also harmful gases like formaldehyde, benzene, ammonia, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These harmful gases are commonly found in everyday life, such as in newly decorated homes, new furniture, and some cleaning products. The role of activated carbon is to capture these pollutants in its vast surface area and prevent them from entering the air we breathe.

Why is Activated Carbon So Important?
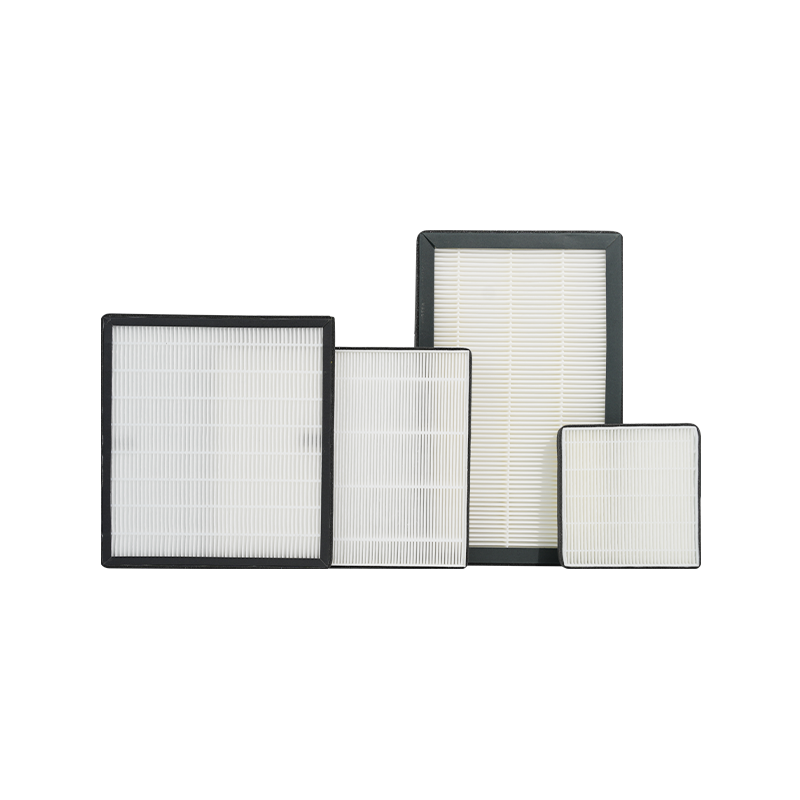
While air purifiers typically feature HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) filters to remove dust, pollen, and other particulates, HEPA filters are relatively ineffective at capturing gases and odors. Many of the indoor air pollutants—such as formaldehyde, benzene, smoke, and odors—are gaseous or volatile, and these substances cannot be effectively filtered by a HEPA filter. This is where the activated carbon filter becomes indispensable. Without it, an air purifier would only address part of the air pollution problem. The combination of HEPA and activated carbon filters is essential for comprehensive air purification.
2. Key Functions of an Activated Carbon Filter
Odor Removal
One of the most well-known functions of activated carbon filters is their ability to eliminate indoor odors. Whether it's cooking smells, bathroom odors, or pet smells, activated carbon is highly effective at capturing and neutralizing these particles through its strong adsorption capacity. This is why it is often referred to as the "soul" of an air purifier—it tackles the most pervasive irritants that impact indoor air quality.
For example, in kitchens where oily foods are prepared, cooking odors can permeate the house and even spread to other rooms. Traditional ventilation systems may not be enough to remove these odors entirely, but an activated carbon filter can effectively capture and remove the smoke and particles in the air, leaving the space smelling fresh.
In households with pets, particularly those with cats or dogs, pet odors—especially urine or body smells—can be a significant problem. Activated carbon filters can capture ammonia and other odor-causing molecules, reducing the unpleasant smells in the air.
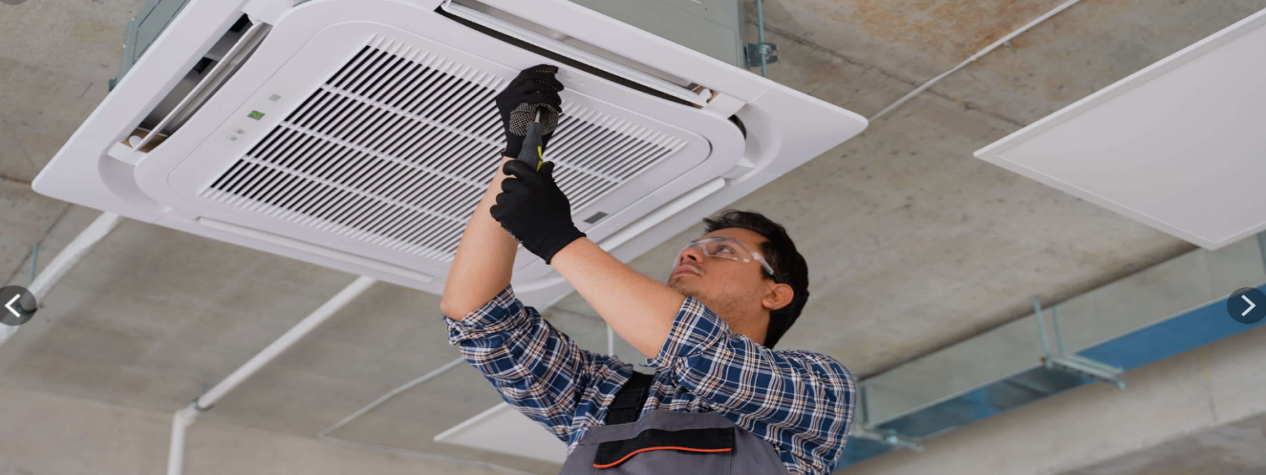

Removal of Harmful Gases
Airborne harmful gases are a major health threat, particularly volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These gases include formaldehyde, benzene, ethanol, and ammonia. VOCs are commonly released from new furniture, paints, cleaning products, and even certain household materials. Long-term exposure to these gases can cause headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, and in some cases, long-term respiratory issues.
Activated carbon filters are highly effective at adsorbing VOCs and other harmful gases, thus reducing the health risks associated with exposure to these chemicals. This is especially important for those living in newly built homes or apartments where chemical pollutants from fresh paint, carpets, or furniture are common. Activated carbon captures these harmful gases before they can cause health problems.
Prevention of Secondary Pollution
Indoor air pollution comes from many sources, and some pollutants can be released back into the air over time. For example, formaldehyde from new furniture or paint may remain in the air for an extended period if not properly filtered, or even re-release into the air. This ongoing release can lead to prolonged exposure to harmful substances.
By continuously capturing harmful gases, activated carbon filters prevent these pollutants from accumulating in the air or being reintroduced, ensuring that indoor air remains fresh and safe for the long term.
3. Why Activated Carbon Filters Are Indispensable in Air Purifiers
The core function of air purifiers is to improve indoor air quality. Many people focus primarily on the HEPA filter and overlook the importance of the activated carbon filter. While HEPA filters are effective at capturing fine particles such as dust, pollen, bacteria, and viruses, they do not effectively remove gases and odors—two major types of pollutants in indoor environments. These gaseous and odorous substances are often the primary sources of indoor air pollution, especially in modern urban living spaces where chemical and industrial pollutants are widespread.
The Complementary Role of HEPA and Activated Carbon Filters
To achieve comprehensive air purification, many high-quality air purifiers combine both HEPA and activated carbon filters. HEPA filters effectively remove airborne particles such as dust, pollen, and microbes, while activated carbon filters target gases and odors. The synergy between these two types of filters ensures that the air purifier can tackle a wide range of indoor air pollutants and provide a more thorough purification effect.
Adapting to Different Indoor Pollution Sources
Activated carbon filters excel in dealing with various indoor pollution sources. Different household environments may face different types of pollutants. For instance, homes with recent renovations may have higher concentrations of formaldehyde, kitchens might have more cooking odors, and pet owners may face pet-related odors. Activated carbon's ability to trap a wide range of gases and pollutants makes it highly adaptable for different situations.
Activated carbon has a significant advantage in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are increasingly common in modern homes due to the presence of synthetic materials in furniture, building materials, and household products.
4. How to Maintain the Effectiveness of Activated Carbon Filters?
Although activated carbon filters are highly effective, their adsorption capacity is limited. Over time, the pollutants they capture saturate their surface, reducing their ability to adsorb additional contaminants. Therefore, regular replacement of the activated carbon filter is essential to maintaining its effectiveness.
Typically, activated carbon filters last 6 months to 1 year, depending on usage frequency, the concentration of pollutants, and the overall air quality in the environment. Many air purifiers come with indicator lights or alerts to notify users when it’s time to replace the filter, ensuring that the purifier continues to function effectively.
To extend the lifespan of an activated carbon filter, it's advisable to avoid using the purifier in highly polluted environments for extended periods. Keeping the indoor environment well-ventilated can also help reduce the concentration of pollutants, thus relieving the filter from excessive strain.

 English
English Español
Español 日本語
日本語